Get in touch
What is DAS
What is DAS
A distributed antenna system (DAS) enhances wireless reception by decentralizing wireless signals: in lieu of using one single tower, a DAS features a series of smaller antennae to power a contained area. A DAS, then, ideally provides stronger and more reliable wireless coverage to concentrated areas such as stadiums, campuses, and hospitals. Today's over-taxed networks caused by the proliferation of smartphones; the lack of cell phone coverage indoors, and the lagged outdoor networks are all predicaments which DAS provides a solution. DAS networks have both an indoor and outdoor application. Additionally, one single DAS network is capable of providing coverage for just one wireless carrier (i.e. Verizon Wireless) or scalable to a network which covers all the major wireless carrier networks (i.e. Verizon Wireless, AT&T Wireless, T-Mobile, Sprint / Nextel), a public safety network, and a private WiFi network. Today wireless networks are not only needed for laptops and cellphones, but many additional systems are in need of wireless connectivity. Devices such as lights, temperature gauges for a broiler room, and even door locks which today can securely be controlled remotely through wireless networks. Many of the latest televisions, home appliances and cars are capable of connecting to wireless networks.
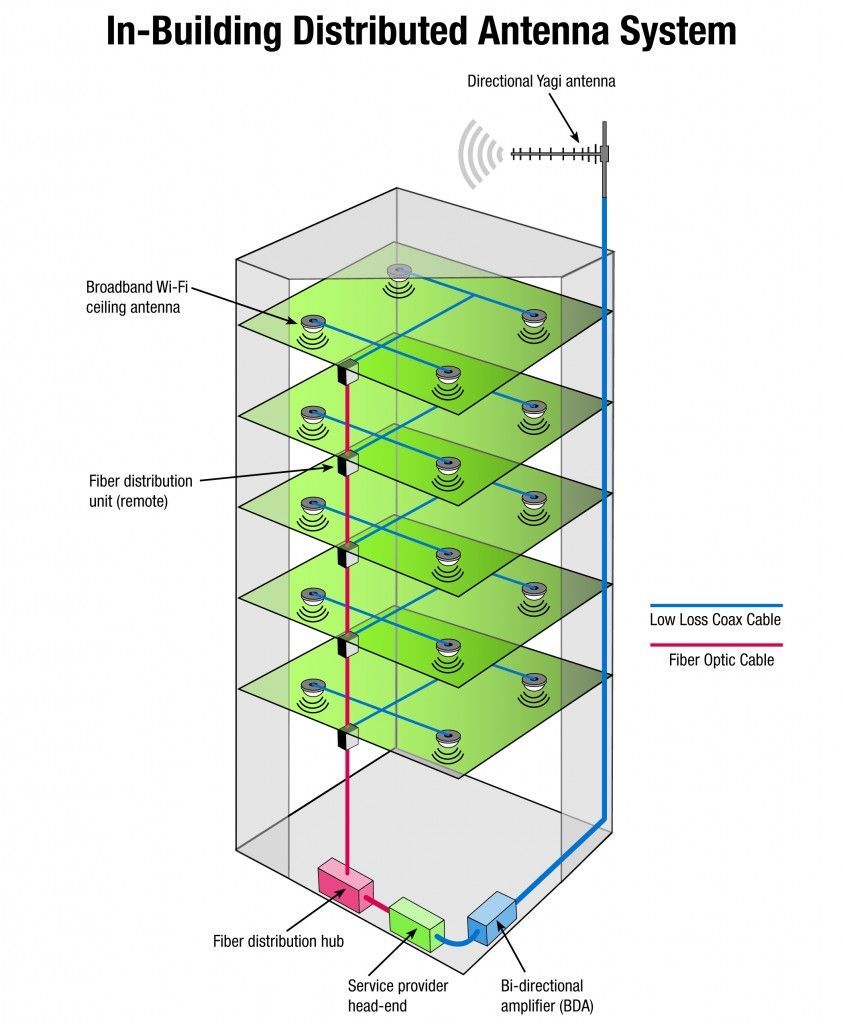
In Building DAS
In-Building DAS (iDAS) is most commonly used to provide wireless reception in buildings and structures which may have inoperative or marginal wireless coverage. These systems can now be used to build out 4-G and even 5-G networks. DAS networks may be used to increase the data capacity of highly-populated indoor facilities, such as a casinos, hotels, hospitals, sports venues and airports. A facility which may have great coverage, but cell phone users have difficulty to make a call, send a text message, and/or browse the internet, would most likely be due to a network capacity constraint.
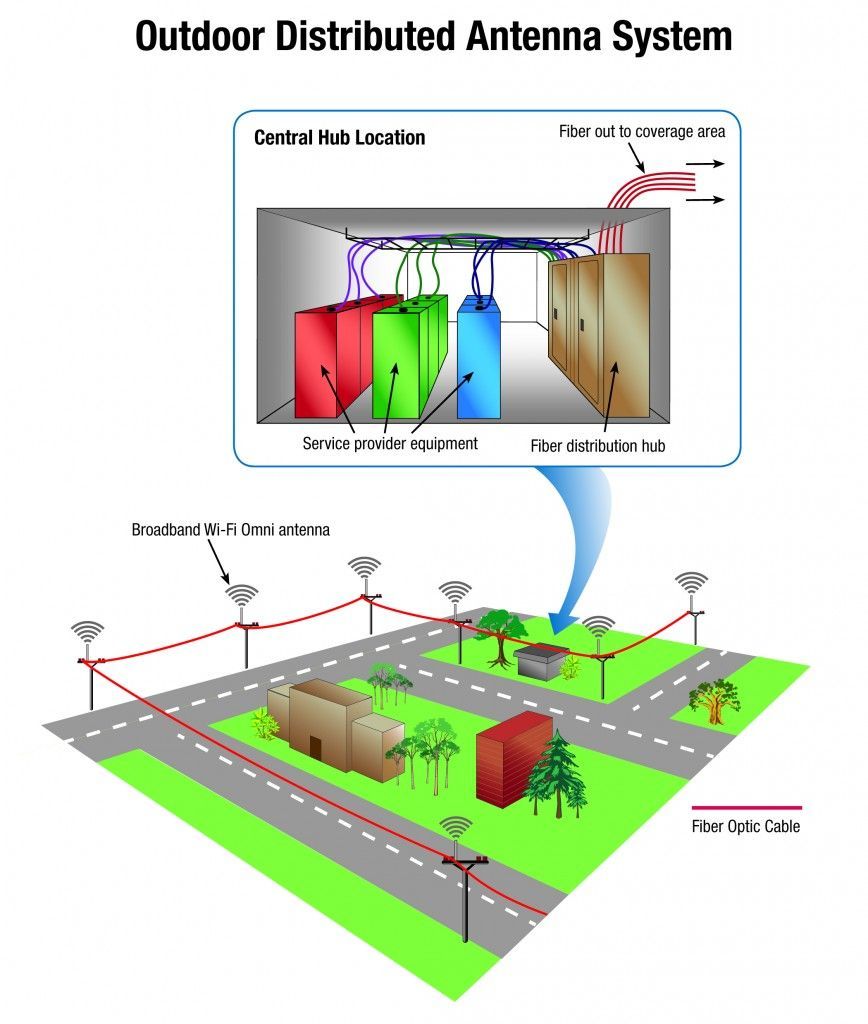
Outdoor DAS
Outdoor DAS (oDAS) are most commonly implemented in locations such as densely populated communities, outdoor coverage gaps too small for traditional cell towers, and communities inimical to cell tower development. Now that over half of Americans own a smart phone, the proliferation of data consumption has caused too much strain on cell towers and other macro cell sites. oDAS offers a cost-effective solution to assist wireless carriers, boost capacity and concurrently improve wireless coverage. oDAS antenna nodes are usually installed to existing street fixtures such as light poles and stoplights.
This is a paragraph. Writing in paragraphs lets visitors find what they are looking for quickly and easily.
This is a paragraph. Writing in paragraphs lets visitors find what they are looking for quickly and easily.
This is a paragraph. Writing in paragraphs lets visitors find what they are looking for quickly and easily.
This is a paragraph. Writing in paragraphs lets visitors find what they are looking for quickly and easily.
This is a paragraph. Writing in paragraphs lets visitors find what they are looking for quickly and easily.
Name Lastname
Title
Name Lastname
Title
Name Lastname
Title




